Subcutaneous parasites, living in the thickness of the human skin, damage it and cause inflammation. They can penetrate from the main place of "deployment" to other organs and provoke serious diseases. Most subcutaneous helminths are found in southern countries, and an ordinary person can become infected with them during a vacation or a business trip there.
The danger of subcutaneous helminthic invasion is that it is asymptomatic during the incubation period, which can last for years. This subsequently interferes with the treatment and reduces its effectiveness.
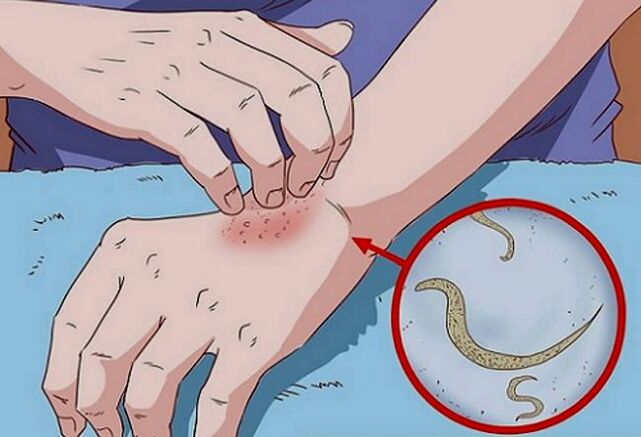
What are subcutaneous parasites
Helminths affect not only the internal organs of a person, but also his skin. Getting into its thickness, they damage the epidermis, feed on its cells and defecate. The waste products of subcutaneous worms cause intoxication, as they contain toxic substances. And the longer the worms are under the skin of a person, the more pronounced the symptoms of invasion.
Subcutaneous worms cause many diseases, as they affect the immune and lymphatic systems of the human body. For example, parasites can provoke the development of elephantism - elephantiasis. It interferes with the circulation of lymph in the body. This leads to an increase in the volume of the limbs and their disfigurement. At the last stage, the affected organ becomes covered with ulcers, necrosis develops.
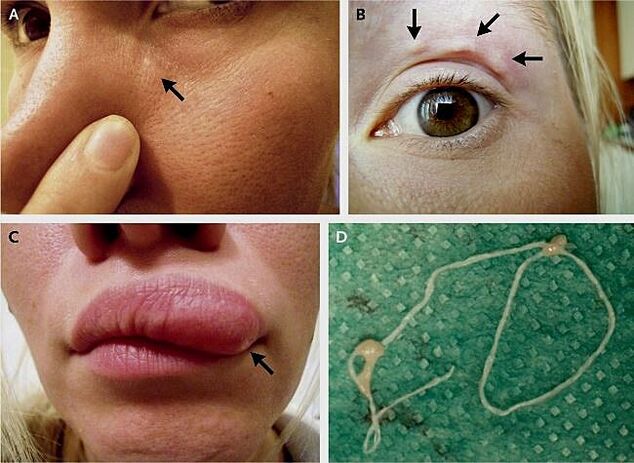
Human helminths that live under the skin include:
- Nematodes of the genus Dirofilaria. Cause dirofilariasis. Infection of the body occurs through the bite of blood-sucking insects: lice, fleas, ticks, which are carriers of larvae from one host to another. An adult dirofilaria can reach 30 cm in length. The process of reproduction occurs in the thickness of the skin, then the female lays microfilariae into the bloodstream.
- Filariae. Cause filariasis. They are parasitic roundworms. An adult can reach almost half a meter, while the body diameter is no more than 0. 3 mm. Carriers of filariasis are blood-sucking insects that transmit parasite larvae from one host to another.
- Bullworm larvae. A person provokes the development of cysticercosis. Infection occurs through the intestines, where parasite eggs penetrate along with water, food, dirt. Subsequently, under the influence of gastric juices, their shell dissolves - the larvae come out. Then they are carried throughout the body along with the blood stream.
- Blood flukes from the genus Schistosoma. It is called schistosomiasis. An adult can reach 2 cm in length. Reproduction occurs through the penetration of larvae into the body - cercariae along with water.
Main manifestations and treatment
If a person has parasites under the skin, then first of all this is reflected in its condition: flabbiness appears, color changes, scars and microcracks appear. This is due to the fact that the "guests" damage the skin, feed on its cells and poison the waste products.
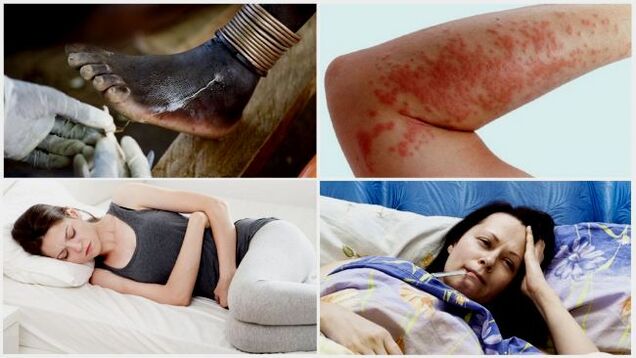
Subcutaneous parasites in humans cause symptoms of helminthic invasion:
- Allergic rashes;
- Cough;
- Decreased immunity;
- Itching;
- Peeling, redness of the skin;
- Appetite problems;
- Pain in joints and muscles;
- Sleep disturbance;
- Irritability;
- Apathy.
Skin parasites in a sick person cause malfunctions of the whole organism: anemia develops, dysbacteriosis, etc.
Treatment of a parasitic disease is selected individually. The choice of method is influenced by the degree of damage to the body, the symptoms and type of pathogen. In some cases, in addition to drug treatment, an operation may be necessary to remove the helminth from under the skin or even the entire organ that has been affected.
Along with antihelminthic drugs, antihistamines, vasoconstrictors are used. If inflammation has begun due to worms living under the skin, then antibiotic therapy is required.
You should not try to get rid of helminths living under the skin with the help of traditional medicine on your own - as practice shows, they are ineffective and can harm human health.
Symptoms of filariasis
The subcutaneous worms that cause this disease - filariae - appear in the human body after the bite of a blood-sucking infected insect. The greatest number of cases is recorded in tropical and subtropical countries.
These subcutaneous worms in humans are able to live in the human body and not manifest themselves for a long time: the incubation period of the disease can last up to 7 years. This makes diagnosis difficult.
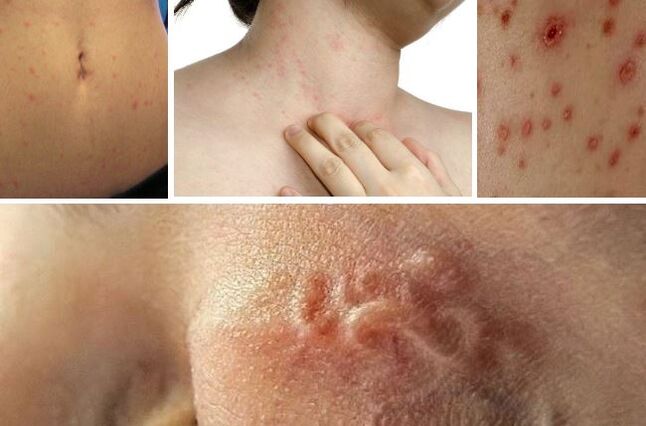
Symptoms and manifestations of invasion appear gradually, as the parasite grows under the skin of a person and its effect on surrounding tissues. The most common manifestations of filariasis include:
- Hives;
- Itching;
- warts;
- eczema;
- Small hard lumps under the skin.
As the disease worsens, fever, general weakness, headache, and drowsiness may occur.
Treatment of filariasis should take place in a hospital setting. For drug deworming, antiparasitic drugs are used. The effectiveness of therapy is monitored by a blood test. In cases where it does not help, a sick person undergoes a surgical operation in order to restore the outflow of lymph from the affected organ.
Cysticercosis and schistosomiasis
The tapeworm larvae cause cysticercosis. This type of helminth is distinguished by survivability: it is enough for one parasite to enter the human body and it will quickly develop into an adult, which will then begin to multiply.
This feature makes it difficult to treat the disease - if the head segment remains after the surgical removal of the worm, the parasite will grow again. Despite the fact that the adult tapeworm is located in the human intestine, its larvae are spread throughout the body with the bloodstream, including under the skin. Subsequently, they can stay there for a long time - from 5 to 30 years.
If, with cysticercosis, the worms are wound up under the skin or in the muscle tissue, then for a person the disease is asymptomatic. However, the location of the parasite can be determined by tumor-like neoplasms that will rise above the skin. On palpation of the tubercle, it can be determined that it is hollow inside. The skin of the shoulders, the upper half of the chest, and the palms usually become a favorite place for the larvae of the tapeworm.
With subcutaneous cysticercosis, medication is not carried out, the patient should be under the supervision of a doctor. This is due to the fact that when the parasite dies after the use of antiparasitic agents, toxins begin to enter the body. They, in turn, can give a strong allergic reaction.
Larvae of schistosomes, cercariae cause schistosomiasis in humans. Infection occurs through water. The first symptoms of worms under the skin appear 10-15 minutes after the invasion. This is due to the fact that the worms under the skin secrete a large amount of their own secretory fluid, which causes a toxic-allergic reaction in a person.
First manifestations:
- Intense itching;
- Hives;
- Rash.
Then there is a lull, after which (after 1-2 months) the acute stage of schistosomiasis begins, which indicates the neglect of the disease:
- Fever;
- Nocturnal hyperhidrosis;
- Hives;
- Dry cough;
- Changes in the qualitative composition of the blood.
At the moment, the treatment of schistosomiasis is limited to the use of 2 anthelmintic drugs. In the acute stage of the disease, steroids, antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs are also used.
Dirofilaria and Morgellon virus
These two diseases have similar symptoms, with some differences. With dirofilariasis, a sick person finds on his body a small tubercle under the skin, which moves during palpation. This is what indicates that a subcutaneous worm has wound up in the body. The same manifestation of invasion is observed with the Morgellon virus.
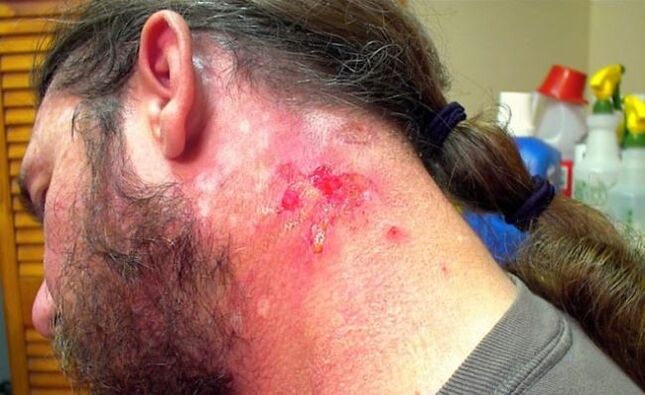
The essential difference between these two parasites is that dirofilaria do not bother their host: the bubble under the skin does not cause discomfort, it can appear and disappear from time to time. Worms parasitize in the arm, leg, near the eyes, nose, on the chest, in men - in the genitals. If dirofilaria is under the skin of a person for a long time, then under the influence of toxins, his body temperature rises and weakness is felt.
With the Morgellon virus, severe itching is felt on the skin of the helminthic invasion. In the absence of medical assistance, a bleeding wound, eczema, soon appears. This increases the risk of infection of the body with other diseases several times.
The best treatment for the parasite is surgical removal.






































